4 management frameworks to help you make your business more efficient
Management frameworks are a number of tools, tasks and processes, implemented for organizing and executing the project from start to finish. Framework describes everything you need for proper planning, management and control of your projects.
In this article you will find product management frameworks picked by Storist that will help you understand clients better, structure the information and increase the effectiveness of product management.
Minimum Viable Product
According to research firm CB Insights, more than 35% of startups have failed because of the lack of demand. There is a solution for minimizing that risk – creating a product with minimal costs, but with numerous functions to attract a target audience.
The strategy of Minimum Viable Product (MVP) will let you get familiar with the market without significant costs and check if there’s demand for your product.
Perfect example of using MVP while launching the business would be Amazon. Jeff Bezos started his business by buying books from suppliers and sending it to clients only when he received an online order. When the company earned some money, they continued developing with the use of MVP. They gradually increased the range of offered goods, opened new warehouses and improved the service.
Eventually Amazon became the company we all know – the world’s largest e-commerce platform.
The term MVP came up in 2001 thanks to Frank Robinson, co-founder and the CEO of the management consulting company SyncDev. MVP management frameworks became massively popular after “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries had been published.

Eric Ries sees the MVP as the experiment on a way to perfection and as essential component of “Build-Measure-Learn” cycle:
- Everything starts with an idea. The idea turns into a hypothesis, stating that this particular idea or a product will be relevant and appreciated by your target audience. Then you Build MVP, which will help you in testing your hypothesis and finding out whether your idea can be successful.
- MVP is tested with your target audience. Their reactions and feedback then get collected and Measured.
Received data is being analyzed, and as a result you get a clear picture and Learn things about your idea and/or product.
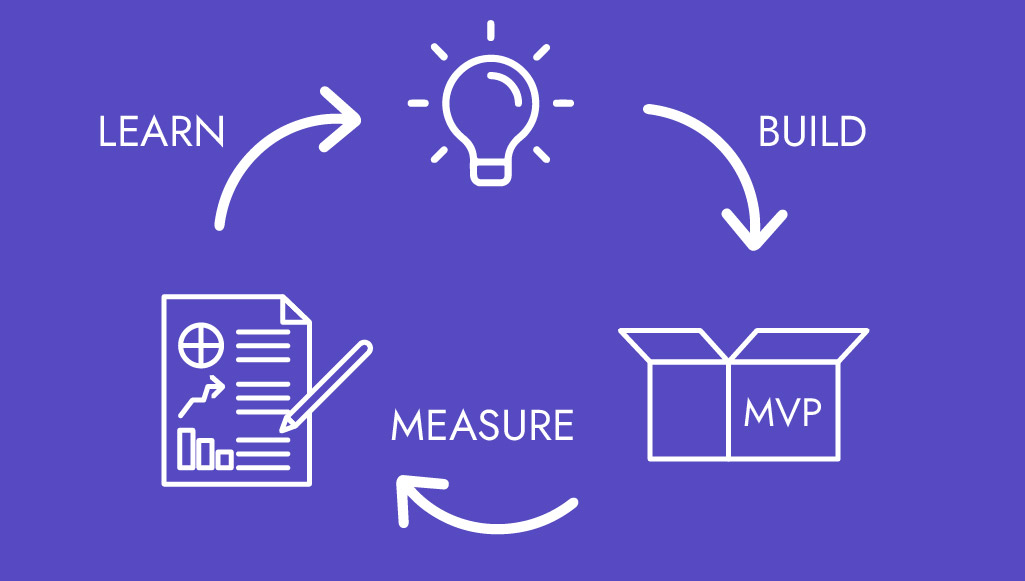
This cycle helps you understand what does your client want and saves both time and resources on developing a product that your client might not even need. You can carry on the “Build-Measure-Learn” process until you get the product, which your client will be excited about.
You can learn more about MVP by completing Storist interactive summary of the book “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries – “Scientific approach to startup development with guaranteed results”.
By finishing the course, you will also learn:
- How to apply in real life the feedback cycle of “Build-Measure-Learn” in order to create an outstanding product
- How to understand your client and his values
- How to create a product that will meet the demand
If you want to understand your clients better and learn to ask the right questions in order to receive the feedback, we can also recommend the interactive summary “How to find out what clients really want?”
North Star Metric
The “North Star Metric” (NSM) term was created and popularized by the founder of GrowthHackers.com Sean Ellis. He states that it is “the single metric that best captures the core value that your product delivers to customers”.
Using this metric allows to reduce administration, to simplify meetings and consolidate a team around specific growth targets.
In order to figure out your North Star Metric, you have to realize first, what value customers get from using your product. Next you need to numerically express this value in one metric. It might be more than one metric, but you have to preferably narrow it down to one NSM. One of the great examples is Spotify and their NSM – “Time spent listening”.
NSM summarizes the core value of the product for your customers. Optimizing your effort on increasing this metric will be the key to gradually building up your client base. Proper NSM is the cornerstone of a successful company and stable business in a long-term perspective.
Job To Be Done
“Jobs To Be Done” (JTBD) is a concept, developed by Bob Moesta and Clayton Christensen for better understanding of the clients’ behavior. JTBD is focused on finding out customers’ needs, and not on the product itself. Understanding the thinking process of your client when he buys something helps you realize what you have to focus on, while creating or updating your product.
Clayton looks at the process of purchasing a product as “hiring” it for a specific task or a need. Like “hiring” a shampoo for washing your hair. If the product does its job well, you are going to “hire” it again when facing the same task. If it does not work well, you will “fire” it and find a replacement.
Jobs To Be Done concept will help you to:
- Understand why the clients buy your product. After analyzing the feedback or polls of your customers, you will be able to figure out which problems does your product solve and what direction you should go.
- Figure out what way your product should change so that people would buy it more often. Developing the strengths of your product will lead you to increasing sales, because it will attract new customers while old customers will stay loyal.
- Develop a strategy that will work. If you figure out the real demand of the target audience, you can build marketing strategy more effectively and be on the same page with your customers. If you want to understand your client better and learn to ask the right questions in order to get the feedback, we recommend our interactive summary “How to find out what clients really want?”.
- Identify which products on the market might be your indirect competitors. If a consumer wants to eat, then Snickers might be an indirect competitor to McDonalds. The product is not the same in any way, but it can be replaced for achieving the same purpose.
With Jobs To Be Done metric you can look at the product from different angle. If you do this on the early stages of creating the product, you will be able to avoid many risks, connected with market entry process. Using JTBD while developing the product will let you be on guard for a moment of changing it according to customers’ needs.
RICE
When you have a lot of projects and ideas, it is crucial to set the priorities right and decide what to start with.
Sean McBride, one of the co-founders of RICE faced the same challenge, when he was a marketing manager. He had the goal of turning the signed up users into actively paying clients. Sean had many ideas on how to do it, but he did not have any means of prioritizing them, except his intuition. At that moment, along with Intercom developer group, he came up with the method, which helped him to increase the conversion up to 28%.
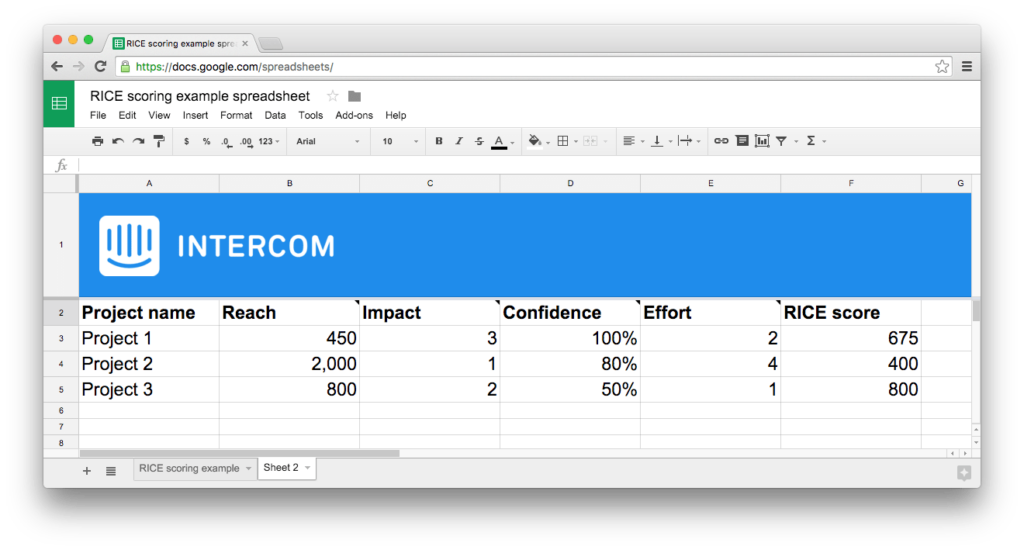
This method was named RICE, consisting of four components: Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort.
- Reach. It is measured in the amount of people/events in a certain period of time. It can be “clients in a calendar quarter” or “transactions in a month”.
- Impact. Focus on projects, which actually get you closer to the goal, influencing your user or clients. Intercom has developed a five-level scoring system, evaluating the impact of the project: 3 = massive impact, 2 = high impact, 1 = medium impact, 0,5 = low impact, 0,25 = minimal impact.
- Confidence. How sure are you of your scores? (100% – high confidence, 80% – medium confidence, 50% – low confidence).
- Effort. How many “person-months” will it take? It is recommended to round the numbers for easier calculation.
After evaluating all four factors use the RICE formula:
(Reach x Impact x Confidence)/Effort=RICE Score
The final score will let you know which project should be given the highest priority.
RICE is one of frequently used product management frameworks, which makes setting priorities easier, but at the same time, it is not a firm and strict rule. There are situations when you can start working on a project with a lower score. For example, if another project depends on its execution. This is fine. But if you have an evaluation system, you can make reasonable decisions on what to work first and sometimes compromise, when it’s necessary.
Business plan
Business frameworks are useful tools that help you analyze business problems and structure your thinking. Product management frameworks are widely used in particular.
If we are talking about business in general, you have to keep in mind such an important element as a business plan. It gives you a step-by-step action plan on effective business management in a long term perspective.
Research results show that more than 30% of small businesses do not survive the first three years without a business plan. Erhan Mollick, the author of “The Unicorn’s Shadow”, also mentions the importance of having a business plan. In his recent Twitter post he wrote:
“Formal startup business plans may have gone out of style, but study after study shows their value: planning ups the chance of business success by 10%-20% or more! Plans help generate agreement, surface assumptions, ensure things aren’t missed, and highlight potential dangers.”
There is no common format of writing the business plan, but you have to remember the key elements:
- Resume. This section contains information about your company and its mission, as well as any data about its executives, employees, production and location.
- Products and services. You can describe products and services provided by your company along with the pricelist, period of validity, and advantages for the customers.
- Market analysis. This part includes information about the company’s competitors and its place in the industry as well as strengths and weaknesses. Write about the anticipated demand for the company’s products and services.
- Marketing strategy. This section breaks down how the company will attract customers, keep the client base and how it is going to win over the consumer.
- Financial planning. This part includes financial planning and company forecasts.
- Budget. This section details all kinds of costs – on staff, development, production, marketing and any other expenses, connected with the business.
Remember that you should not spend too much time and energy on too much of a detailed document. Its main purpose is to specify the focus, the scale and the area of business of the company.
Checklist
One more effective way of saving time and money is a habit of making checklists.
This is a simple solution for complicated or repetitive tasks. By making lists, you will get the plain and quick instrument, which will help you avoid missing any elements while executing the task.
Good checklists do not include the smallest details; they only serve as a reminder for each key step. The simpler they are to use, the more effectively they will work.
Storist knows how important and convenient it is to use checklists, so in each of our summaries you will find unique and useful sets of checklists and templates. We call those sets handbooks. Join Storist and get access not only to interactive summaries based on the best inspirational and educational business books, but also to the sets of manuals that will assist you in solving everyday tasks.