How the GIST framework allows you to abandon outdated product roadmaps
GIST is a convenient framework that allows you to abandon product roadmaps, Gantt charts and product strategies.
GIST was invented by product manager Itamar Gilad, who held senior positions in product management at Google, Microsoft and other well-known companies for 15 years.
The framework allows you to:
- Flexibly adjust plans to the current moment;
- Reduce management costs;
- Improve team performance;
- Improve communication between departments;
- Make better products and solutions.
How to use it
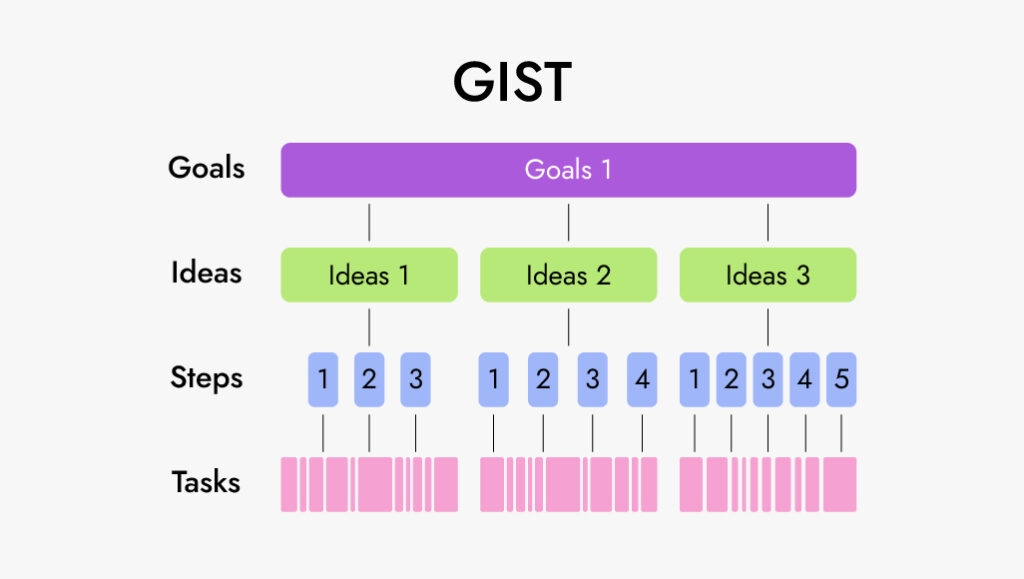
The system is called GIST by the first letters of its main blocks:
- Goals
- Ideas
- Step-projects
- Tasks
Each stage has multiple deadlines for execution and planning. In addition, different tools are used at each stage. However, the consistent implementation of all steps helps to achieve outstanding results.
Goals
The author of the methodology emphasizes that most strategies focus on solving specific tasks: entering into a partnership, entering the market with the release of a product, etc. The disadvantage of this approach is that tasks quickly become obsolete. In order to solve this problem, Gilad suggests using the Goals and Key Results Methodology (OKR) and focusing on goals.
Goals describe the company’s strategy in terms of desired results:
- Where do we want to be?
- When and how will we know that we have achieved them?
The OKR system is one of the factors that makes Google a successful company
Ideas
Ideas are a potential way to achieve results. It is a normal situation when out of several dozen ideas, only a few are useful. And often the value of an idea is not immediately obvious.
Therefore, in GIST you need to follow several rules:
- Do not give up ideas in advance
- Do not remove ideas with low priority
- Do not prioritize ideas from status employees
- All ideas are put into the idea bank, most often in a spreadsheet or database
- Ideas are prioritized based on facts. For example, the ICE scoring method is well suited for this
- As many ideas as possible are tested in order of priority
Step-projects
A typical mistake of project managers is to choose one idea and focus on it. Often after a few months it turns out that the idea is outdated or was initially wrong.
Instead, we break up a large project into small projects that last no more than 10 weeks, and execute them in turn. For example:
Detailed Static Prototype → Interactive Prototype → MVP → DogFood → Beta → Launch
According to the «Build-Measure-Learn» principle in Lean Startup, each such project is actually an experiment that tests an idea. That is, with each project we get a more complete version of the idea and test it on a wider audience for an increasingly long time.

There are many advantages to this approach.
- The final product is usually better than the original idea
- A lot of ideas can be tested simultaneously and with lower investments
- Non-working ideas are eliminated early, and ideas that work get more investment
- The team feels better, as ideas are implemented into the product within a couple of weeks after their development.
Tasks
Then each project is divided into tasks. There are many management systems on the market that support various development methodologies: Scrum, Kanban or others. Choose any system in which it is convenient for you to work.
What planning looks like
- Goals are usually set with an eye to one year or several years. The goals are determined at the beginning of the year and adjusted every quarter
- Ideas are constantly being collected and prioritized. The search for them never stops.
- Projects are determined at the beginning of the quarter. The team selects the goals and ideas that it wants to accomplish this quarter, and determines the projects accordingly. The quarterly list of projects is evaluated and re-prioritized once every 1-2 weeks and synchronized with the task list.
- Tasks are divided into 1-2 week iterations according to your method of development work and adjusted daily.

Example
Let’s analyze the framework using the example of a startup that runs an application with meditations
Goals
For setting goals we will use the OKR method
O. Reach payback by the end of 2024
KR 1. Increase the number of subscribers by 1000 users monthly
KR 2. Increase the average subscriber’s check by 100%
Ideas
Then, for each KR, we come up with ideas for implementation and prioritize them.
Ideas for KR 1
- Attract paid traffic from Google
- Launch an advertising campaign with the participation of celebrities
- Enter into partnership agreements with a network of fitness centers
Ideas for KR 2
- Give bonuses for the purchase of new meditations in the app
- Expand the product line
- On behalf of the company offer users to transfer part of the amount for the purchase of the second meditation to charity
Projects
At this stage, ideas turn into short projects that are quickly tested.
For KR 1
1.Attract paid traffic from Google
Study the tools, issue a key message, conduct a test campaign, calculate the price of a subscriber.
2. Launch an advertising campaign with the participation of celebrities
Make a list of celebrities, agree on cooperation, design creatives, publish messages, analyze the effectiveness.
3. Enter into partnership agreements with a network of fitness centers
Make a list of partners, develop an affiliate program, agree on terms, launch, evaluate the results.
For KR 2
1. Give bonuses for the purchase of new meditations in the app
Develop the logic of issuing bonuses, develop a technical solution, launch, analyze the results.
2. Expand the product line
Make a list of ideas for new meditations, select three ideas, make a test product, launch, evaluate the results.
3. On behalf of the company offer users to transfer part of the amount for the purchase of the second meditation to charity
Conduct custdevs with users, make a list of partners, launch, evaluate the results.
Tasks
Further, each project is divided into tasks in any planning system convenient for you and then implemented.
Takeaway
This framework allows you to quickly and flexibly implement new products, constantly adapting to the market. If you want to learn more about useful product management tools, check our blog.