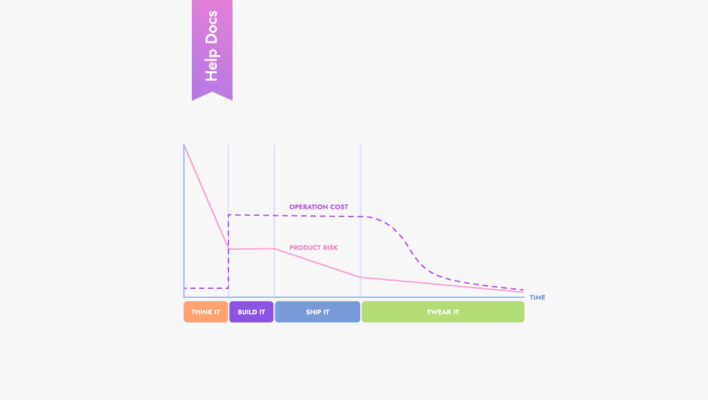
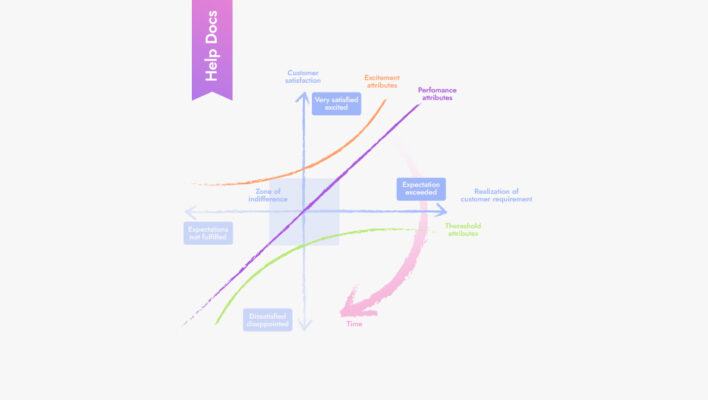
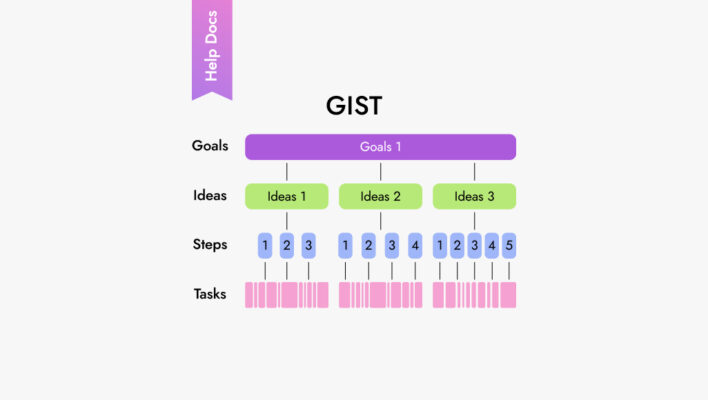
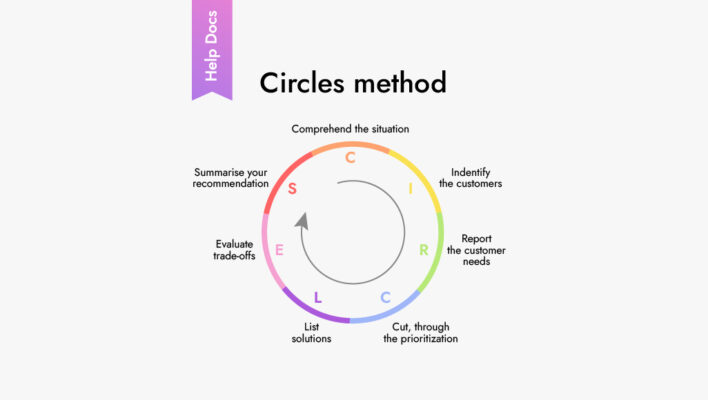
What kind of product management frameworks will help you operate more efficiently and develop projects?
Developing a successful product requires more than just a great idea. It takes a well-structured plan, clear objectives, and a systematic approach to product development. That’s where using a framework in product management can play a huge role. Not only does it help teams to work more efficiently and make informed decisions, but it also stimulates collaboration and ensures that everyone is working on the same goals.

In this article, you can take a closer look at the benefits of using a framework in product management and how it can help you turn your ideas into successful products that your customers will love.
Design Sprint Framework
The Design Sprint framework has become an important tool for many companies looking to validate ideas, solve problems quickly and increase innovation. Developed by Google Ventures designers Jake Knapp, John Zeratsky and Braden Kowitz, the structured product development framework is presented in the book “Sprint: How to Solve Big Problems and Test New Ideas in Just Five Days”. This unique framework is now widely used across various industries by companies of all sizes. The big idea with the Design Sprint is to build and test a prototype in just five days.
The sprint process includes the following steps:
- Map. In the first step of a Design Sprint, the team maps out the problem they are trying to solve and identifies the key contributors and potential user personas. This helps the team to get a better understanding of the problem and the context in which it exists.
- Sketch. In the sketching phase, the team generates a wide range of ideas and possible solutions to the problem. Each team member sketches their ideas on paper, using a technique known as “crazy eights,” which involves folding a piece of paper into eight panels and sketching an idea in each panel within a limited time frame.
- Decide. The team then narrows down the ideas to a select few that they want to pursue further. They use criteria such as feasibility, desirability, and viability to make the decision.
- Prototype. In the prototyping phase, the team builds a simple prototype of the selected ideas, using tools such as paper, pen, and sticky notes or digital tools such as Figma or Sketch. The goal is to create a prototype that is just realistic enough to test with users.
- Test. In the testing phase, the team tests the prototypes with real users, collecting feedback and insights in order to adjust the next iteration of the design. The team observes how users interact with the prototype and asks them questions to understand their experience and any pain points.
With these steps, the Design Sprint framework helps teams to quickly prototype and validate new product ideas, reduce the time and cost associated with traditional product development cycles, and create products that are more likely to meet the needs of customers and be successful in the market.
SCAMPER framework
SCAMPER is an effective product development process that encourages creative thinking and the exploration of problems. It is also an invaluable tool in helping problem-solving and improving product performance, as it helps identify any inefficiencies or areas where a product can be modified or improved. Through SCAMPER, you can not only produce innovative ideas, but also increase the efficiency of your product creation process.
SCAMPER is an acronym, where each letter represents a different strategy or question to induce creative thinking:
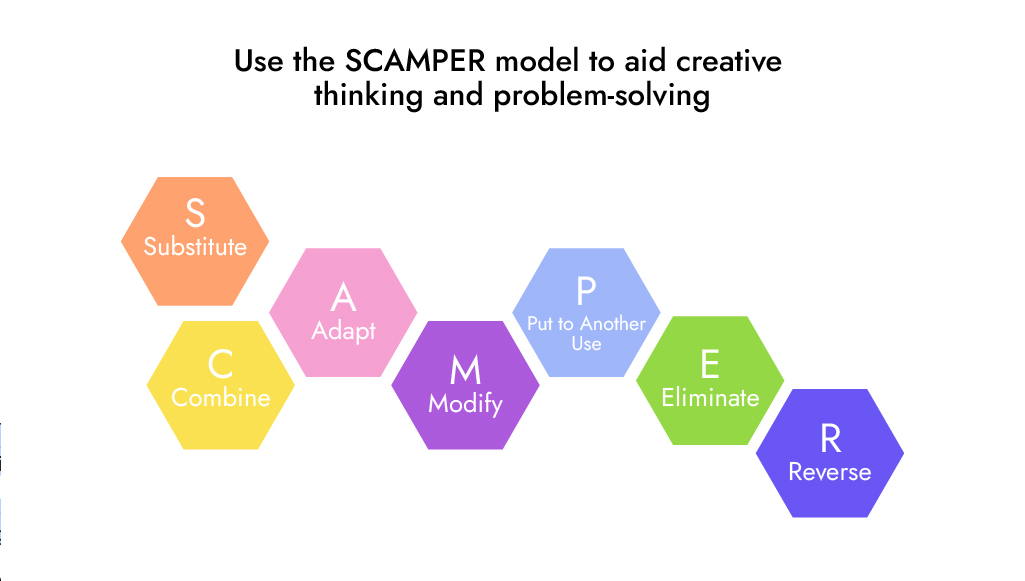
- Substitute
One way to come up with new ideas is to substitute something in the existing product or service. For example, if you’re a clothing company, you could substitute different materials in your clothing items to make them more environmentally friendly. Or else, you could substitute a delivery method to make it more convenient for customers.
- Combine
Another way to come up with new ideas is to combine two or more existing products or services. For example, you could combine a clothing company with a home decor company to create a new type of store that sells both clothes and home goods. You could also combine a restaurant with a delivery service to create a new type of business that delivers meals to customers’ homes.
- Adapt
Another option is to adapt an existing product or service to meet the needs of a different market. For example, you could take an existing product and modify it to be used by a different age group. Furthermore, you can take an existing service and adjust it to be used in another location.
- Modify
Modifying an existing product or service is another way to come up with new ideas. For example, you could redesign a clothing item to make it more comfortable or stylish. You could also change a restaurant dish to make it healthier.
- Put to Other Uses
Putting an existing product or service to other uses is a new way to generate fresh ideas. On the one hand, you could use a clothing item as a decoration for your home. On the other hand, you can turn a restaurant dish into a part of a catering menu.
- Eliminate
Eliminating some aspects or elements from an existing product or service can also help to generate new ideas. For instance, if you remove certain ingredients from the recipe to make the dish healthier. Or if you get rid of certain features in a piece of clothing to make it more affordable
SCAMPER is one of the techniques that Michael Michalko presents in the book “Thinkertoys.” And you can also fulfill the true potential of your creativity and innovation skills! Storist interactive summary will take you on a journey through the exciting world of “Thinkertoys” by Michael Michalko. You’ll discover a treasure trove of creative problem-solving techniques. Join us today and start working on your inner innovator with the Storist.

North Star Metric
The North Star Metric is a tool companies use to help align their teams and initiatives around a shared vision and purpose. It was originally popularized by Sean Ellis, the founder of GrowthHackers.com, an online platform for growth-focused entrepreneurs, marketers, and product managers that are seeking to share knowledge, collaborate, and learn from each other. The NSM has been adopted by many companies as a guiding principle for their business strategies.
The North Star Metric framework can significantly improve product planning. The idea is simple: first, identify a single, overarching goal that everyone can work towards in the organization. This goal should be measurable and aspirational, so that its progress would be easy to track. It will act as a guiding star for all departments and teams to strive for success. After identifying the singular goal, teams and departments within the organization can develop smaller sub-goals that align with this bigger purpose. This allows every team to take ownership of their goals while working together with a common objective they can all benefit from.
Whether it is launching a new app or revamping an existing website, the North Star Metric can equip your team with consistent decision-making criteria that bring you results.
Here are some examples of North Star Metrics from successful companies:
| Company | North Star Metric |
| Airbnb | Nights booked |
| Daily active users (DAUs) | |
| Spotify | Time spent listening |
| Netflix | User retention |
| Monthly active users (MAUs) |
Job To Be Done
The “Job to be Done” (JTBD) framework is a powerful approach to understanding customer needs and designing products that meet them. The JTBD framework is fundamentally based on the idea that customers “hire” products to help them accomplish specific tasks. In order to apply the JTBD framework, product managers must first identify the tasks that their customers are trying to accomplish. This requires a deep understanding of customer needs and desires as well as a willingness to think outside the box and challenge assumptions.
One of the key benefits of the JTBD framework is that it encourages product managers to focus on the results rather than features. Instead of simply adding more and more features to a product, product managers can use the JTBD framework to design products that meet specific customer needs and deliver measurable results. This leads to more effective and efficient products that are likely to be successful on the market.
If you want to identify, comprehend and meet your customers’ needs more effectively, then our interactive summary “How to find out what clients really want?” is just the tool for you. It is based on ideas from the book by Rob Fitzpatrick, “The Mom Test: How to Talk to Customers & Learn If Your Business Is a Good Idea When Everyone Is Lying To You”, an invaluable source that has become one of the most popular books for product managers. (books for product managers)
HADI Cycle
Using the HADI Cycle framework can bring several benefits to product managers. First, it helps to ensure that you thoroughly analyze the market and your target audience before investing significant resources into the development process. By using a data-driven approach, you will be able to identify and prioritize the most important qualities of your customers. Secondly, if you prototype and test your product before launching, it will reduce the risk of getting a product that doesn’t meet customer needs.
HADI stands for Hypothesize, Analyze, Design, and Implement. Here’s a brief overview of each step:
- Hypothesize.
Thinking critically about the desired outcome is one of the most important tasks in a project plan. In this stage, you generate hypotheses about the results your project needs to accomplish and what resources it will require. This involves identifying the problem you’re trying to solve, defining your target audience, and knowing your project goals.
- Analyze
This stage of the HADI cycle involves doing market research, such as surveying current customers and gathering feedback, utilizing industry-specific data to understand key trends and competitive insights, assessing customer needs and preferences, understanding buying behavior, analyzing past sales figures and more. Accurate analysis of all this data will help you choose which hypotheses should be tested first in an effort to gain reliable results.
- Design
In this stage, you use the insights gathered in the previous step in order to design your product or project. This includes creating a prototype, modeling the user experience, and outlining the project plan.
- Implement
Finally, you implement your project plan and launch your product or service. This involves testing your product, making any necessary changes, and deploying it to your target audience.
Building strong relationships, learning analytical skills, understanding customer needs and using appropriate frameworks – all these aspects are essential for managing a product. If you are an aspiring product manager and start to develop these skills, you will be in an excellent position to succeed.If you’re looking to take your product management skills to the next level, “The Lean Startup” is the book for you! With its powerful insights, practical advice, and inspiring success stories, this book will help you build products that truly make a difference. Don’t wait – join the Storist interactive summary service and start transforming your approach to product development.