Identify the root cause of a problem and fix it with 5 Whys technique
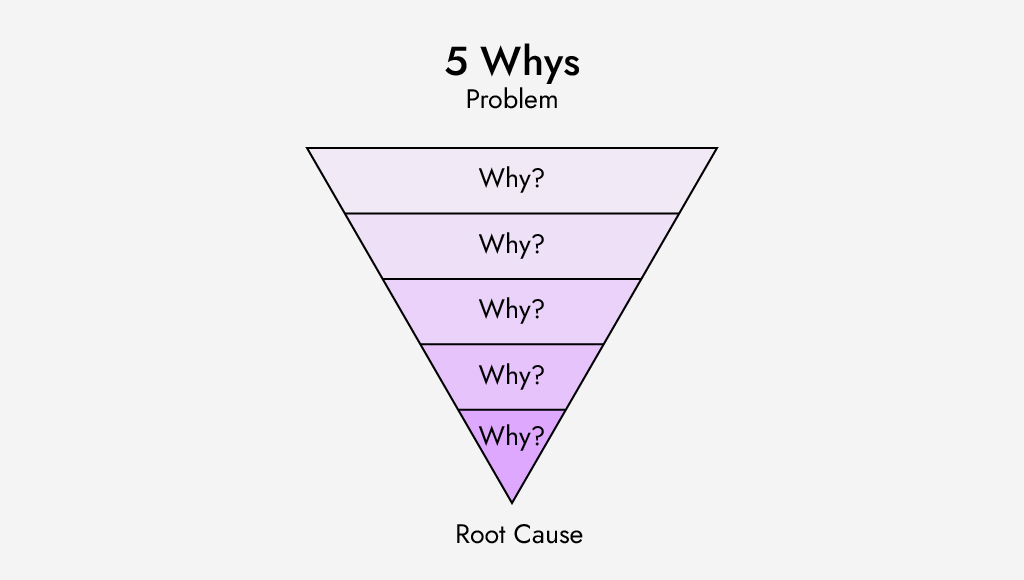
The 5 Whys technique is a powerful way to identify the root cause of a problem by asking “why?” five times and discovering the hidden causes and solutions.
The Five Whys technique is an iterative interrogative technique to explore the cause-and-effect relationships underlying a particular problem.
The technique was invented by Sakichi Toyoda, who used it to enhance his company’s production methods. It is a key part of the Toyota Production System (TPS), a lean
manufacturing system that strives to reduce waste and increase efficiency in production processes.
The Five Whys technique can be used in a business setting to analyze the root cause of issues related to quality control, process improvement, customer complaints, project delays, and safety incidents. It helps businesses understand underlying problems and implement effective solutions.
How to use it
To conduct the 5 Whys analysis, you need to:
1. Assemble a team
The first step is to gather a team of people familiar with the problem or with different perspectives. Ideally, you want to include people who have practical experience or expertise in the area where the problem occurred. A diverse team can help you avoid biases and assumptions and generate more insights and ideas.
For example, if the problem is related to customer service, you may want to include customer service representatives, managers, product developers, and marketers. If the problem is
related to software development, you may want to include developers, testers, designers, and users.
2. Identify the problem
The next step is clearly defining and agreeing on the problem you want to solve. You can use a problem statement or a question to describe the issue in simple and specific terms. For example, “We didn’t send the newsletter about the latest software updates on time”. Ensure everyone on the team understands and agrees on the problem before moving on.
3. Start asking “Why”
Begin the inquiry by asking “Why?” to determine what caused the problem. The initial answer may not be enough to explain the whole problem, so you need to keep asking “Why?” until you reach a deeper level of understanding. Avoid asking too many Whys. If you do, you may encounter many unreasonable proposals and complaints, which is not the intention. Focus on finding the root cause.
Advice 1. Use a brainstorming method to generate multiple possible solutions and explore different perspectives. For example, you might use a mind map, fishbone diagram, or SWOT analysis to organize your ideas and identify the most likely cause of the problem.
Advice 2. The 5 Ways technique can help you solve problems quickly and efficiently, improve your processes, and prevent the recurrence of issues. However, this analytical tool can have limitations and challenges, such as oversimplification, bias, divergence, validation, and control. To overcome these challenges, follow some best practices, such as using data and evidence, asking open-ended questions, including diverse perspectives, using complementary tools, and focusing on the most significant or actionable root cause.
4. Make an action plan
Once you have identified the root cause of the problem, you can devise an action plan to address it and prevent it from happening again.
5. Monitor the Effects
You should also evaluate your action plan to see if it effectively solves the problem. Use metrics, surveys, feedback, or other methods to measure your results and adjust as needed.
Example
Here is an example of how to use 5 Whys in a real case situation:
Problem: The customer satisfaction score for our online store has dropped by 10% in the last month.
- Q: Why has the customer satisfaction score dropped by 10%?
A: Because we received more complaints about delayed deliveries and damaged products.
- Q: Why did we receive more complaints about delayed deliveries and damaged products?
A: Because our shipping partner had some operational issues and mishandled some of our packages.
- Q: Why did our shipping partner have some operational issues and mishandle some of our packages?
A: Because they were understaffed and overloaded with orders due to the holiday season.
- Q: Why were they understaffed and overloaded with orders?
A: They did not anticipate the surge in demand and needed to hire more workers or expand their capacity.
- Q: Why did they not anticipate the surge in demand and hire enough workers or expand their capacity?
A: They did not communicate with us or other clients about their forecasts and plans.
Root cause: The lack of communication between our shipping partner and us or other clients caused them to be unprepared for the surge in demand, resulting in delayed deliveries and damaged products, which lowered our customer satisfaction score.
Action plan:
- Contact our shipping partner to discuss improving their communication and planning processes.
- Look for alternative or backup shipping partners in case of emergencies. We can also apologize to our customers and offer them discounts or refunds for their inconvenience.
- Monitor our customer feedback and satisfaction score more closely and take corrective actions.
Takeaway
The Five Ways method helps find the root cause of a problem and solve it effectively. This problem-solving technique can save time and resources, improve business processes, and increase customer satisfaction. The 5 Whys technique can also help you develop critical thinking, logical reasoning, and collaboration skills.