The best solution can be calculated! Decision Matrices will help you consider all important factors
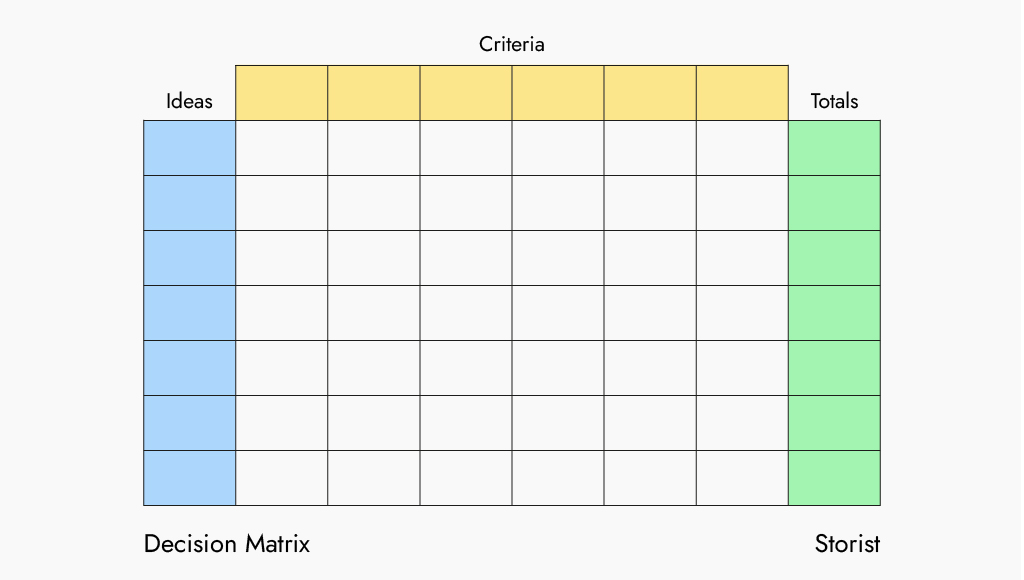
Decision Matrix
The Decision Matrix is a tool used to evaluate and prioritize different options or alternatives based on a certain criteria.
The origins of the decision matrix can be traced back to the military operations research, which emerged during World War II. The method was developed by a team of scientists and mathematicians who were assigned to find ways of optimizing military operations. Over time, the weighted decision matrix has been adapted and refined by various researchers and specialists in such fields as business, engineering, and healthcare. Today, it is a widely used tool for decision-making in many different contexts.
The Decision Matrix typically involves creating a table with each option listed in rows and each criteria listed in columns. Each cell in the table is then filled in with a score or rating based on how well the option performs for that particular criteria.
The scores are usually numerical values or qualitative ratings such as “excellent,” “good,” “fair,” or “poor.” Once all cells are filled in, the scores for each option are added up, and the highest-scoring option is considered the best choice.The Decision Matrix is often used in business and project management to make complex decisions when multiple options and factors have to be considered. It provides a systematic and objective approach to decision-making and can help ensure that all relevant criteria are taken into account.
How to use it
These are the general steps to creating a decision matrix for any decision-making process:
1. Identify the decision: Determine the problem that needs to be solved or the decision that needs to be made.
2. Define the criteria: Determine the factors or criteria that will be used for evaluating the options. These criteria should be measurable and relevant to the decision.
3. Assign weights to the criteria: Assign weights to each criteria based on its relative importance in the decision-making process. The weights should add up to 100%.
4. List the options: Identify the different options or alternatives that are available to solve the problem or make the decision.
5. Rate each option: Rate each option in every criteria, using a scale or scoring system that reflects how well the option satisfies the criteria. This can be done by assigning a numerical value, using a ranking system, or by simply indicating whether the option meets the criteria.
6. Multiply the ratings by the weights: Multiply each rating by its corresponding weight for each criteria.
7. Put the scores together: Add up the scores to determine the total results for each option.
8. Pick the best option: Choose the option with the highest score.
It’s important to note that the Decision Matrix is only a tool to assist decision-making and should not be used as the sole basis for making a decision. Other factors such as cost, feasibility, and risks should also be taken into consideration.

Example
Here’s an example of how the Decision Matrix could be engineered to assist the decision-making process
Let’s say a company needs to choose a new supplier of a particular material. They have identified three potential suppliers and have defined three criteria that are important to them: cost, quality, and delivery time. The weights assigned to each criteria are 40%, 30%, and 30% respectively.
In order to create the decision matrix, they would list the three suppliers in rows and the three criteria in columns. They would then rate each supplier in each column, using a numerical scale from 1 to 5, with 5 being the highest score.
Here’s an example of what this Decision Matrix might look like:
| Supplier | Cost (40%) | Quality (30%) | Delivery Time (30%) | Weighted Score |
| A | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4.1 |
| B | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4.0 |
| C | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3.9 |
To calculate the weighted score, the company would multiply each rating by its corresponding weight and then add up the products for each supplier. In this example, Supplier A has the highest weighted score and would be the best choice based on the defined criteria.
Of course, there may be other factors that the company needs to consider before making a final decision, but the decision matrix provides a useful starting point for evaluating the possible options.
Takeaway
Improving your soft skills can have a significant impact on your professional and personal success. By developing your communication, problem-solving, critical thinking, emotional intelligence, time management, leadership, and adaptability, you can become a more effective decision-maker, build stronger relationships, and achieve your goals more efficiently.
Join Storist’s interactive book summary to learn from leading business books, gain valuable insights, and improve your soft skills.